Since Nextcloud has released the High Performance Backend as OpenSource under AGPL License, i tried my luck to install it on Ubuntu without docker, but many people had problems or run other OS as Ubuntu/Debian and asked „what about docker?“. Ok, without is a little bit tricky, so let us go with docker:
Requirements:
– a VPS with docker and docker-compose (Tested on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 LTS) (you can get one here @netcup with 5€ Discount or start at Hetzner Cloud with 20€ start credits)
– shell access and appropriate rights
– One DNS A and possibly AAAA record for our nginx vhost and stun/turn-server (I use signaling.example.com for all three services in this guide)
– Optional – a second DNS A and possibly AAAA record for stun/turnserver
Hardware Requirements:
4 CPU
8 GB RAM
32 GB Disk-Space
See also: Nextcloud Portal
You can also test a smaller server if you don’t have that many users
Step 1: Install Firewall and other packages
First of all, you should install a firewall to secure your VPS (if not installed) and allow incoming traffic to port 80/443, 22 (ssh) and for coturn on port 3478tcp/udp only. For Securing ssh-access you can use fail2ban and passwordless authentication. Many guides for this are out there.
apt install ufw -y ufw allow http ufw allow https ufw allow ssh ufw allow 3478/tcp ufw allow 3478/udp ufw enable
Accept with „y“
Step 2: Install git, docker and docker-compose
Install docker:
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | CHANNEL=stable sh systemctl enable docker.service systemctl start docker.service
and now docker-compose and git with:
sudo apt install -y docker-compose git
Step 3: Clone git-Repository and build Images
we clone the git-Repository to /opt
cd /opt/ git clone https://github.com/strukturag/nextcloud-spreed-signaling.git && cd nextcloud-spreed-signaling
create a random hex key (STATIC_SECRET) for your nextcloud talk app and signaling server with:
openssl rand -hex 32
and a hashkey:
openssl rand -base64 16
a blockkey:
openssl rand -base64 16
a Nextcloud SHARED_SECRET for Signaling:
openssl rand -hex 16
an API-KEY:
openssl rand -base64 16
and copy all for later use, then edit docker-compose.yml
nano docker-compose.yml
adjust the following entries REALM and STATIC_SECRET:
version: '3'
services:
spreedbackend:
build: .
volumes:
- ./server.conf:/config/server.conf
network_mode: host
restart: unless-stopped
depends_on:
- nats
- janus
- coturn
nats:
image: nats:2.1
volumes:
- ./gnatsd.conf:/config/gnatsd.conf
command: ["-c", "/config/gnatsd.conf"]
network_mode: host
restart: unless-stopped
janus:
build: docker/janus
command: ["janus", "--full-trickle"]
network_mode: host
restart: unless-stopped
coturn:
build: docker/coturn
network_mode: host
environment:
REALM: signaling.example.com
STATIC_SECRET: openssl rand -hex 32
restart: unless-stopped
then generate server.conf:
nano server.conf
and copy and paste the following (please adjust your backends and secrets):
[http] listen = 127.0.0.1:8080 [app] debug = false [sessions] hashkey = openssl rand -base64 16 blockkey = openssl rand -base64 16 [backend] backends = backend-1 #here you can add more backends commaseparated backend-1, backend-2, backend-3 allowall = false timeout = 10 connectionsperhost = 8 [backend-1] url = https://nextcloud.example.com secret = openssl rand -hex 16 #[backend-2] #url = https://nextcloud2.example.com #secret = openssl rand -hex 16 #[backend-3] #url = https://nextcloud3.example.com #secret = openssl rand -hex 16 [nats] url = nats://localhost:4222 [mcu] type = janus url = ws://localhost:8188 [turn] apikey = openssl rand -base64 16 secret = openssl rand -hex 32 servers = turn:localhost:3478?transport=udp,turn:localhost:3478?transport=tcp
save file and change rights to 644:
chmod 644 server.conf
and then build the images:
docker-compose build
you have to wait a little bit before you can continue.
then bring the complete stack up with:
docker-compose up -d
now you should have at least 4 containers running:
docker ps
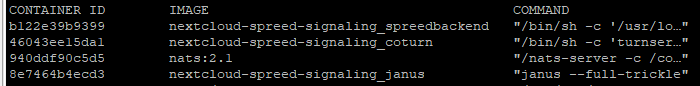
then go to next step.
Step 4: Install nginx and create vHost for signaling server
Now we will install nginx as reverse proxy for our high performance backend:
apt install nginx python3-certbot-nginx -y
and create the vHost:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/signaling
copy, paste and adjust:
server {
listen 80;
server_name signaling.example.com;
}
and activate vhost:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/signaling /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/signaling
then check with:
nginx -t
and reload
systemctl reload nginx
now use certbot to obtain a certificate:
certbot --authenticator standalone --installer nginx -d signaling.example.com --pre-hook "service nginx stop" --post-hook "service nginx start"
then paste the following config in the vHost-conf:
mv /etc/nginx/sites-available/signaling /tmp/signaling.bak && nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/signaling
upstream signaling {
server 127.0.0.1:8080;
}
server {
server_name signaling.example.com;
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/signaling.example.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/signaling.example.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains; preload";
location /standalone-signaling/ {
proxy_pass http://signaling/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
location /standalone-signaling/spreed {
proxy_pass http://signaling/spreed;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
server {
if ($host = signaling.example.com) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name signaling.example.com;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
and check an reload nginx:
nginx -t
if ok
systemctl reload nginx
Step 5: Configure nextcloud to use stun/turn and signaling server
Now we are ready to add turn/stun- and signaling-server to our Nextcloud
Go to Settings, Talk and enter the following:
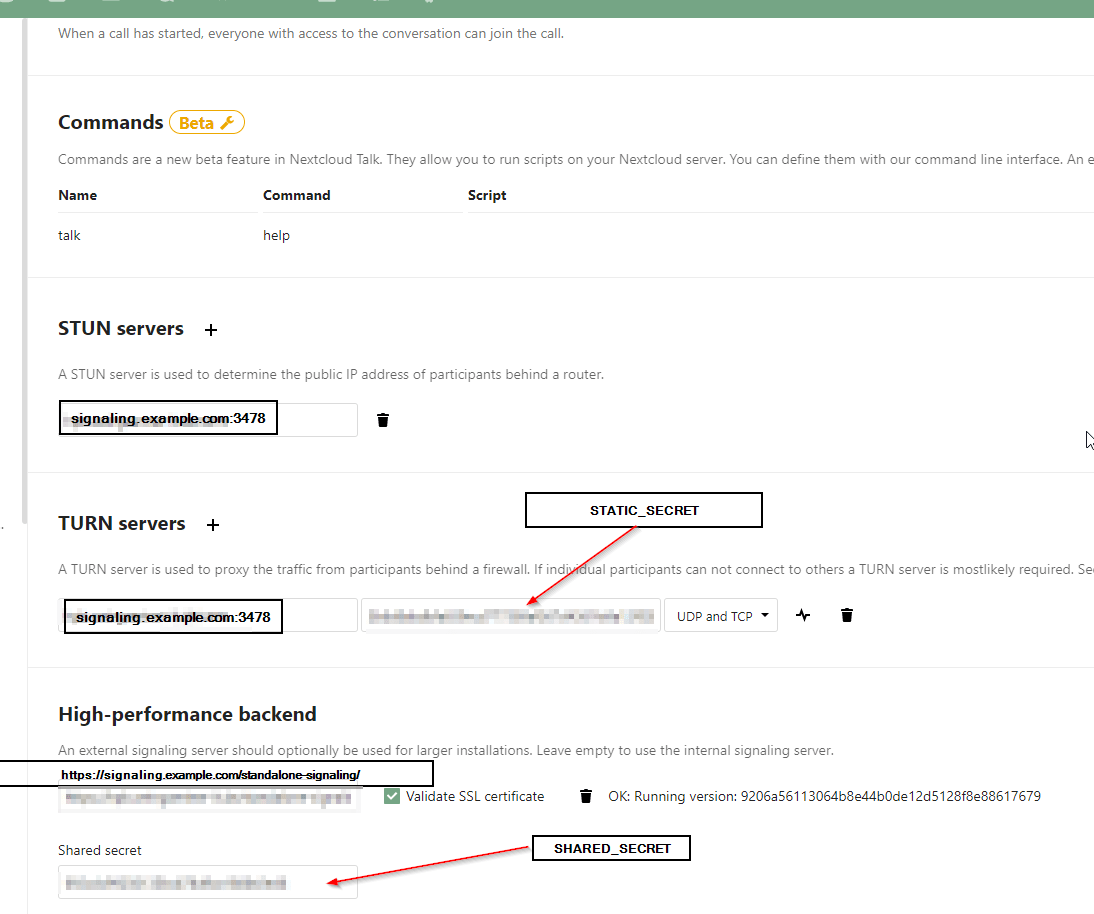
And then enjoy your High Performance Backend.
Problems with the tutorial? Then comment below or contact me per Mail or Mastodon.
I will be happy if you would support my work here.
Happy nextclouding and do not forget to share ?
If you want to try an easier solution look at this deeztek @ github
Sources:
Picture from Alexandra_Koch on Pixabay
Struktur AG
Tested on netcup
Tested on Hetzner Cloud
